The impact of manufacturing activities on the global environment is becoming noteworthy, and effective waste reduction and energy conservation technologies are urgently needed in manufacturing processes to achieve sustainable development. The majority of manufacturing processes involve welding processes ranging from traditional to recent manufacturing technologies.
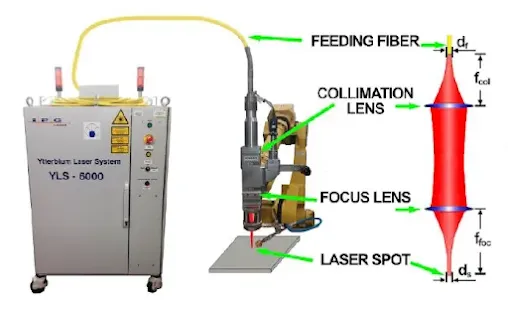
Nowadays, laser welding is the most popular method in the manufacturing industry, and it is used on a wide range of materials and products. Laser welding is the most advanced process. Very low heat input to the weld, low distortion and the ability to weld heat-sensitive components are the advantages of laser welding. The selection of input parameters is critical for obtaining good weld bead geometry.
Laser Beam Welding
The joining technique is one of the vital manufacturing techniques that may be utilized to enhance product design and reduce production costs. Laser beam welding uses gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). Welding is the process the accurate, reliable, and economical process of joining the two work-pieces together. Also, it has below characterizations,
Excellent quality
High performance
High precision
High speed
Good flexibility
Minimal distortion
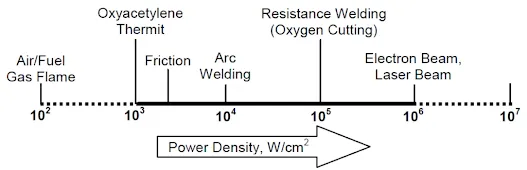
The power density of the laser beam is shown below,
| Characteristic | Note |
|---|---|
| The high density of energy | Minimum distortion |
| Speedy processing | Economical (if fully utilized) |
| Sudden start/stop | Because this process is operated by a CNC programme |
| Atmospheric pressure welds | Compared to arc procedures and electron beam welding |
| No X-rays are produced | Versus welding with an electron beam |
| No need for filling (Autogenous weld) | Failing to remove the flow |
| Confined weld | Minimal distortion |
| Zone with very little Heat Affected | Weld is performed near heat-sensitive materials |
| It is possible to weld quite precisely | Weld can be done from low to high workpiece |
| Excellent weld bead profile | There is no need to clean up |
| In a magnetic field, a beam cannot stray | As opposed to electron beam welding |
| Without contamination | Relying on gas obscuration |
| Rarely can difficult materials be welded | General benefit |
Laser Welding Types
CO2 Laser
The process has little heat input and excessive density of energy which is generated using the continuous wave of CO2. This type of laser welding produces a tiny heat-affected zone (HAZ), which cools more speedily with less disfigurement and has a high depth/width ratio for the fusion area.
The primary outcome of the procedure is the CO2 laser strengthens the plume of the welding above the joint by diffusing the power density of the beam, reducing the weld depth and enhancing the weld joint’s surface breadth. Traditionally, CO2 lasers have been used for applications related to automobiles.
There are a number of benefits,
Quick
Repeatable
Long weld with high-quality
Straight seams
Can weld axisymmetric components
Neodymium yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) Laser
The solid-state laser crystal known as neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet, or Nd: YAG, is extensively employed in a variety of applications. This laser gets its name from the dopant (neodymium) and the host crystal (YAG). Recent developments in Nd: YAG laser technology have made it possible to transmit beam energies of at least 2 kW across fibre optic cables. Particularly beneficial for robotic operations where the laser beam must be manipulated around a stationary part.
Nd: YAG laser beam welding is a high energy density and low heat input process that causes a small heat-affected zone (HAZ), which has a high ratio between depth and width for the fusion zone and cools more quickly with minimum distortion.
Fibre Laser Welding
Diode Lasers
Weld defects
Weld pool pores
Undercutting
Undercutting is a major defect and it happens when the weld edge is below the weld center. The difference between the maximum and minimum points of the weld surface is considered the undercutting. Undercutting may occur irregularly while increasing the speed of the weld using the pulsed laser.
Humping
This is a longitudinal weld defect and can be identified as Consistent bumping and limitation of the face of the weld. The metal from the weld develops humps above the workpiece's surface. This defect may occur at high velocities and the weld pool shape is important in the formation of the lift of the weld.
Blow-holes
Cracks
Non-uniformity and surface roughness
Limitation of Laser Welding Process
Only applicable to metals and alloys
Application of Laser Welding Process
Automotive Industry for body, chassis, exhaust system, powertrain components weld




0 Comments: