Design:
The design of the desired object is created as a digital 3D model using 3D modelling software or by scanning an existing object using 3D scanners. This file is saved in STL file format.
Slicing:
This process is done to divide the digital model into thin, horizontal layers. A set of instructions (G-code) which is used to guide the 3D printer is created by this software.
Printing:
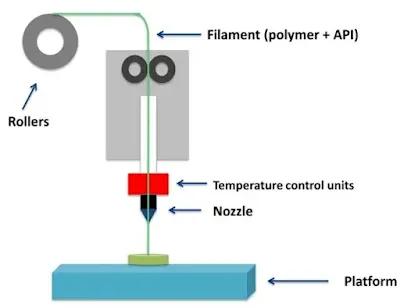
The 3D printer uses the G-code to add material layer by layer. There are plenty of popular materials for the 3D printing process, such as plastics (like PLA and ABS), metals, ceramics, and even organic materials like living tissue in bioprinting. Depending on the kind of material, the printer's print head or nozzle will either heat or cool it before depositing it onto the build platform or earlier layers.
Cooling and Solidification:
The printed 3D model cools and solidifies after each layer is deposited. Some materials solidify instantly, while other materials may need post-processing operations, such as oven baking or UV curing.
Support Structures:
Sometimes, support structures may be used to prevent sagging or collapsing during the printing process for some model which has an overhang or complex geometries. These supports are usually removed after printing is complete.
Finishing:
Once the object is fully printed, it may require post-processing steps like sanding, painting, or assembly. This is done according to the desired final product.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are few 3D printing technologies. In this section, these technologies are described briefly.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling is one of the most popular 3D printing methods and is widely used in 3D printing technology. This is referred to as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). It is used for melting and extruding thermoplastic materials through a nozzle to build the object layer by layer. FDM is a cost-effective, simple, accessible, and versatile process. However, it has a few limitations, such as layer lines and visible print lines on the surface of the printed object, which may require post-processing to achieve a smoother finish. Mainly it is used for prototyping, hobbyists, and small-scale production.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is also an additive manufacturing process which is used to build high-precision, detailed, and complex three-dimensional objects with smooth surfaces using liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer. Mainly it is used for prototypes, dental models, jewellery, and custom medical devices. However, SLA 3D printers and the associated resins tend to be more expensive than some other 3D printing technologies like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an advanced additive manufacturing process. It uses a high-powered laser to sinter or fuse fine powdered materials to create strong, durable and complex 3D objects using plastics or metals. SLS is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and heat resistance for aerospace, automotive, and healthcare industries.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
The Digital Light Processing method is similar to Stereolithography (SLA) but uses digital micro-mirror devices (DMDs) and a light source to create highly detailed three-dimensional objects with smooth surfaces. DLP is a speed and precision process for projection displays and 3D printing resin-based objects. It is used for crucial applications, such as dental, jewellery, and custom manufacturing industries.
PolyJet
Polyjet uses liquid photopolymer resin to build highly detailed, multi-material, and multi-colour parts. This machine cures layers using UV light. It can create products with aesthetics, high levels of visual and functional realism and fine details, such as product design, automotive design, architecture, and the production of consumer goods. However, it may not be the ideal choice for parts requiring high heat resistance or extreme durability.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting is a method of layer-by-layer construction in which a liquid binder is selectively injected into a powder bed to bind particles together. This method is frequently used to create full-colour items that resemble sandstone.
Material for 3D Printing
Plastics: PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), commonly used for FDM printers.
Advantages of the 3D Printing Process
Cost-effective
Highly customization
Limitations of the 3D Printing Process
Applications of 3D Printing Process
Aerospace: Producing lightweight components for aircraft and spacecraft.










0 Comments: