Shall we consider why a differential is needed for an automobile? A traditional differential is a gear train with three shafts that has the property that the angular velocity of one shaft is the average of the angular velocities of the others. In automobiles, the differential allows the outer drive wheel to rotate faster than the inner drive wheel during a turn. This is necessary when the vehicle takes turns, making the wheel that is travelling around the outside of the turning curve roll farther and faster than the other.
Classification of differential in automobile applications
Automobile manufacturers have developed several types of differential in the world to achieve various tasks such as improving traction between tire and road and stability control. The following types are the most common types of differential in day automobile applications.
Open differential
Locking differential
Limited-slip differential
Torsen Differential
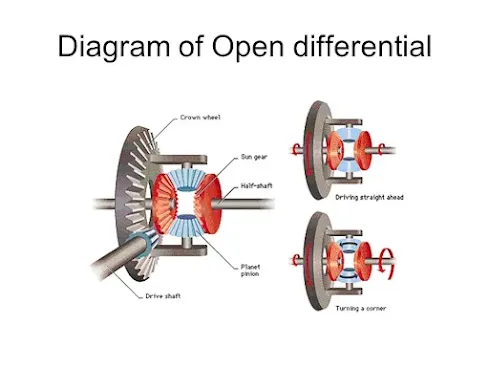
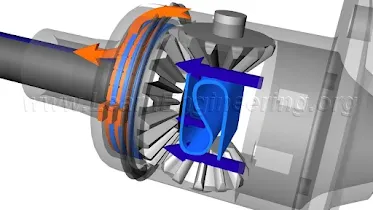
Open differential
The open differential is a type of differential that supplies the same amount of torque to each of the wheels of a vehicle. The differential splits Engine torque into two output shafts. The output shaft can be rotated at different speeds.
Shortcomings of open differentials
Traction is determining the amount of torque that is supplied for the wheels. The engine can limit the amount of traction needed on hard. In slippery, wet or unstable surfaces, torque is applied so that traction can be achieved without risking slippage. When one wheel has steady traction and another is at risk of slipping, the differential divides the torque between both wheels, reducing the torque for the stable wheel to that of the slipping one. This has the disadvantage of reducing revolutions per minute (rpm) to zero.
1. Great on roads
2. Predictable power distribution on the dry surface
3. Easy to drive and handle simplicity of design
4. Lower maintenance cost
Disadvantages
1. Poor off-road handling
2. Unpredictable power distribution on lower friction surfaces
Locking differential
The locking differential is an improvement of the open-type differential. A locking differential provides increased traction than an open differential by restricting each of the two wheels on an axle to the same rotational speed without regard to available traction or differences in resistance seen at each wheel. There are two types of lockers
1. Automatic locker
2. Selectable locker
Automatic locker
Automatic lockers lock and unlock automatically with no direct input from the driver. During ordinary conditions, when the vehicle is driving a straight road, the differential at “lock” state and if the difference between the speeds of the two rear wheels is minimal to the specified limit no signal will be generated by the electronic circuit. They will never allow either wheel to spin slower than the differential carrier.
Selectable locker
Selectable lockers allow the driver to lock and unlock the differential at will from the driver's seat. This can be accomplished in many ways.
1. Compressed air (pneumatics).
2. A cable cable-operated mechanism is employed.
The shortcoming of locking differential
Locking the differential on a high-grip surface such as dry pavement makes it difficult to turn the vehicle. Increased tire wear and noticeable impact on driving behaviour. During cornering, which half-axle is uncoupled is dependent on the torque direction applied by the driveline. In selectable locker Mechanically complex with more parts to fail. Needs human interaction and forward-thinking regarding upcoming terrain.
Advantages
1. Traction is maximum due to both wheels providing high force with the same speed
2. Simple
3. Robust
4. No electronic controllers
Disadvantages
1. More expensive
2. Limited slip during engagement
3. Driver needs to manually engage
4. Some systems may be complex
Limited slip differential
Limited slip differentials (LSD) are used in vehicles to overcome the traction difference problem of drive wheels. Two types of limited slip differential are commonly used in automobiles.
1. Clutch Plate Limited Slip Differentials
2. Viscous Limited Slip Differential
Clutch Plate Limited Slip Differentials
Viscous Limited Slip differential
In this kind of differentials hydrodynamic friction from fluids with high viscosity is used to transfer engine power to drive wheels. Silicon base fluids are normally used as fluid. Here, a cylindrical chamber of fluid filled with a stack of perforated discs rotates with the normal motion of the output shafts.
Advantages
1. Smooth torque transfer
2. Easy to drive
3. More proportional response due to slip
4. Limited "wind up" at low speed
Disadvantages
1. Fluid can break down with time
2. Less efficient than a conventional differential
3. Higher associated maintenance
4. Delay response due to viscous fluid is a flexible medium.
Torsen Differential
The Torsen differential is a generous method that provides differential effects and overcomes traction difference problems. There are some components other than traditional open differential. There are six warm and wheel sets as shown figure.
1. Mechanical Simplicity
2. Less maintenance
3. Continuous Torque Transfer
4. No need for driver input
Disadvantages
1. High manufacturing cost2. Limited slip but not locking
3. More complexity





0 Comments: