Forming is the one of manufacturing methods which is used to make some objectives. Metal forming is the metalworking process that is used to form metal parts for different shapes through deformation. The material piece is reshaped without adding or removing material.
Hot Forming
The hot hot-forming process is used very frequently to cast industrial products and parts. The
raw materials are available form of sheets, tubes, bars or wire. In this process,
heat is applied to the material to soften. Then, some of the required pressure is
applied to get the desired shape of the metal. This process is also capable of forming a variety of complex parts and holds relatively tight tolerances.
Most hot-forming processes are complex due to the involvement of adiabatic heating, die chill
and microstructural changes.
Hot
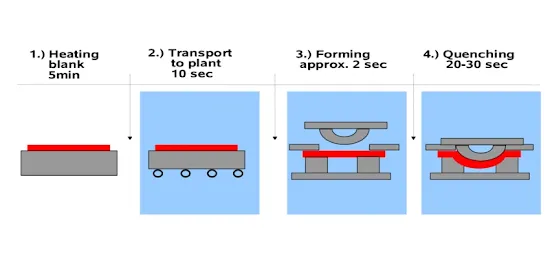
hot-forming process is one of sheet forming processes of sheet metal. This process
is also known as hot stamping or press hardening. All forming processes are run
above the recrystallization temperature of the material. The material recovers
and softness during the hot forming process of sheet metal. The hot sheet metal
is brought into contact with the hot die and a hot punch is pressed into the die to form
the shape and then apply forming pressure for a period.
A direct (one-stage) hot-forming process is commonly used due to forming and part hardening
being done in one operation.
|
Advantages of hot forming |
Disadvantages of hot forming |
|
Accurate forming |
Burr formation |
|
Complex shapes |
Furnaces cause high energy cost |
|
Consistent thickness |
The surface finish is poor |
|
Higher surface profile tolerances |
The component can wrapped in the worst-case |
|
Resistance to cracking |
The surface of the component
slightly scaled due to the high working temperature |
|
Good strength |
|
|
Lower cost |
|
|
Low spring back |
|
The uses of the hot-forming process are as below,
In the automobile industry: -
Side members, door reinforcements, sills, roof frames, roof
rails, and bumper supports.
Cold Forming
The cold forming process is the metal forging
process at bear room temperature or slightly above room temperature. Forming
metal at cooler temperatures may retain or enhance the tensile strength of the
material. This process is a high-speed process that allows the manufacture of large
amounts of metal-based products in a fast, consistent and cost-effective way. Cold-formed parts have greater yield, higher
tensile strength and superior surface finish when compared to hot-formed parts.
The cold-forming process can be classified into
four major groups, such as squeezing, bending, drawing, and shearing. However,
higher loads are required to do the cold forming process and deformation is low compared hot forming process. Also, a high degree of manufacturing experience is
required to achieve complex geometry parts.
|
Advantages of Cold-forming |
Disadvantages of Cold forming |
|
No heat is required, so low energy is required |
Harder tools and dies are needed due to metal is
harder |
|
Better surface
finish |
Low
deformation |
|
Superior
dimensional accuracy |
Material with
low ductility cannot be sold formed. |
|
Improve
strength properties |
Metal surfaces
must be clean and scale-free |
|
Contamination
problems are minimized |
Residual
stress may occur |
|
Material
savings & elimination of scrap |
Higher forces
required for deformation |
|
Inexpensive |
|
|
Big production
rate and long life |
|
|
Material
savings & elimination of scrap |
|
Fasteners, screws, nuts, bolts, electrical
contacts, and rivets
Warm Forming
Warm forming is the metal deform process in which metal is heated to a temperature that maximizes the material's malleability without allowing re-crystallization, grain growth, or metallurgical fracture. Warm forming aims to combine the strong points of hot and cold forming. Better surface finishes can be achieved than hot forming. Temperature control is difficult in this process. If more complex parts are formed, precision is low. The warm-forming process is suitable for medium-scale productions.
|
Advantages of Warm forming |
Disadvantages of Warm forming |
|
Reduce tooling loads
compared to cold-forming |
Lower precision than cold forming
|
|
Increased
steel ductility |
Strict temperature control |
|
Lesser amount of heat energy requirement than hot forming |
Greater press loads than hot forming |
|
Lesser thermal
shock on tooling than hot forming |
Required
skilled engineering to design appropriate tooling |
|
Better dimensional control than hot forming |
|
|
Better
precision components than hot forming |
|
In the automotive industry,
warm-formed parts are used (Door panels, fenders). In such applications, warm
forming of certain aluminium alloys may be cost-effective because of reduced
vehicle weight and fuel consumption.
.webp)





0 Comments: